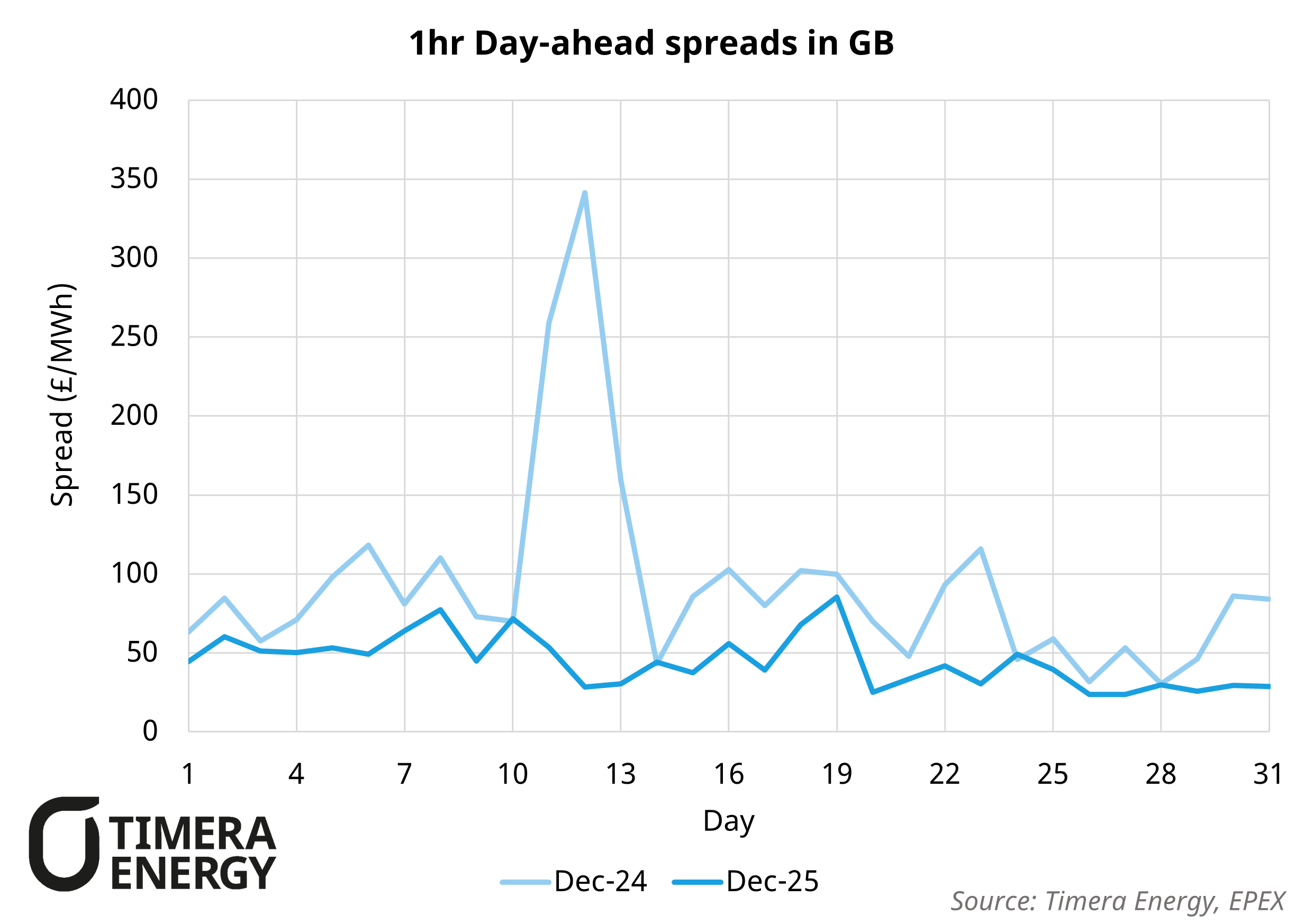
December 2024 was a standout month for GB BESS, providing a welcome break from the generally muted returns seen through the rest of 2024 and setting the tone for stronger performance into early 2025. By contrast, December 2025 revenues have been around 40% lower than December 2024, driven by three main factors:
- No Dunkelflaute driven volatility: In December 2024, a pronounced Dunkelflaute (low wind coinciding with higher demand) tightened the system and materially increased price volatility, with day ahead spreads reaching ~£340/MWh. December 2025 has been characterised by a milder winter and fewer sustained low wind periods, limiting volatility and capping spreads and therefore reducing arbitrage margins for BESS.
- Lower gas prices: Gas prices were higher in December 2024, supported by colder weather and stronger heating demand. In December 2025, prices have been ~34% lower than in Dec24, as increased US LNG supply & weaker Asian LNG demand have driven a looser market. Gas price dynamics remain a key swing factor for GB power volatility and BESS value over the next 3–5 years as we transition into a more structurally oversupplied gas regime.
- Ancillary price decline: December 2024 followed the launch of Quick Reserve, a new ancillary product well suited to BESS. As is typical with new services, initial pricing was elevated while participation was limited. Through 2025, as the service has matured and entry has increased, prices have compressed from ~£8–9/MW/h in December 2024 to ~£3–4/MW/h in December 2025. This is consistent with a rapidly scaling BESS fleet, where supply growth is expected to outpace growth in ancillary demand. Going forward ancillaries are projected to increasingly play a supporting role to wholesale trading strategies rather than acting as a primary revenue source.
- Congestion supports value: In December 2025, Scottish BESS outperformed non-Scottish assets despite the weaker revenue environment, capturing additional BM value driven by congestion behind the B6 and B4 boundaries adding ~5-15% to revenues. In contrast, December 2024 revenues were more heavily driven by arbitrage and day ahead spreads, meaning location played a less material role in performance.
The comparison of Dec-24 to Dec 25 reinforces a core feature of BESS & general flex asset economics: revenues are highly exposed to weather, demand and commodity price drivers, resulting in inherently volatile cashflows. At Timera we address this explicitly using stochastic modelling to quantify both expected returns and downside risk, click here to learn more about our approach.
If you’d like to discuss our views on GB or European BESS markets, or learn more about our stochastic modelling approach please reach out to Arshpreet Dhatt, Senior analyst (arshpreet.dhatt@timera-energy.com) to arrange a call with our team.